
Neuro Linguistic Programming
Some Basic Concepts in Neuro-Linguistic Programming
by Tad James, M.S., Ph.D., Certified NLP Master Trainer Copyright © 1985, 1999, 2012
Neuro-Linguistic Programming (NLP) is about noticing patterns. So, in NLP, we are not so much interested in content as in process. Often this is an interesting transition for us to make. The first step is to pay attention to the process of your interaction with others — listen to the form, watch the form, feel the form, and not get involved in the content.
What’s the Difference Between Content and Process?
First of all in life, most people tend to focus or to pay attention to content. If you ask them what happened they will give you all the details. The more they investigate a subject they will get more and more into the details. They will finally get lost in the proverbial forest because of all the trees.
We could, however, put our attention in an opposite direction and look toward the bigger picture. If we did that we might, just might, see the interconnections between the details at which we had been looking. When we look at the bigger picture and find the interconnections we are finding patterns. We are looking at the process or the structure of the details. We could then begin to see the patterns.
You may have heard that Neuro-Linguistic Programming (NLP) is about noticing patterns. So, the NLP Coach is not as much interested in content as in process. The first step is to pay attention to the process of your interaction with others watch the patterns, listen to the structure, feel the process and do not get involved in the content. Because so many people are oriented to content, this can be a really interesting transition for us to make in our thinking. Of course, the next question then is how specifically do you “watch the patterns, listen to the structure, feel the process and do not get involved in the content?”
THE MODALITIES of NEURO LINGUISTIC PROGRAMMING
The modalities are one way of categorizing exactly what a person does inside their head as they think. They are a way of looking at process, or a model of what a person does in their head as they put together an Internal Representation (I/R).
In the process of creating Neuro Linguistic Programming, NLP discovered that by looking at someone else’s eyes as they move, you could tell HOW they think. Not what they think, but HOW they think. You can tell what they’re doing inside.
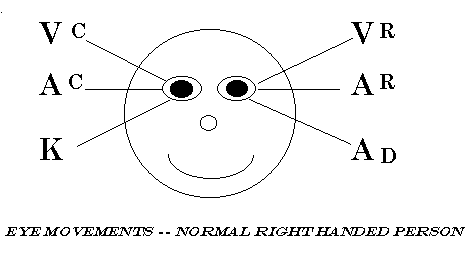
Based on initial observations in NLP, when people look up, they’re visualizing. When they look horizontally to the left and right, they’re either remembering or constructing sounds. When they look downward and to our left, they’re accessing their feelings. And when they look downward and to our right, they’re talking to themselves (Auditory Digital). The chart above is for a “normally organized” right handed person. Many left-handed people and some ambidextrous people will have eye movements that are reversed from this.
Vr Visual Remembered
(Visual Recall) – Seeing images from the memory, recalling things you’re have seen before. QUESTION: “What color was the room you grew up in?” “What color is your bedroom now?” “What does your coat look like?” (In addition, some people access visually by defocusing their eyes. When this happens, the eyes will usually stay in the center.)
Vc Visual Constructed
(Visual Created) – Images of things that you have never seen before. When you are making it up in their head, you are using Visual Constructed.
QUESTION: “What would your room at home look like if it were blue?” “What would your dog look like if it had the head of an elephant?”
Ar Auditory Remembered
(Auditory Recall) – Is when you remember sounds or voices that you’ve heard before or things that you’ve said to yourself before. When you ask someone, “What was the very last thing I said, they typically look in that direction.
QUESTION: “Can you remember the sound of your mother’s voice?”
Ac Auditory Constructed
(Auditory Created) – Is making up sounds that you’ve not heard before. For example
QUESTION: “What would I sound like if I had Donald Duck’s voice?” “What would Swan Lake sound like if it were played on bagpipes?”
K Kinesthetic
(Feelings, Sense of Touch) – You generally look in this direction when you’re accessing your feelings
QUESTION: “What does it feel like to touch that rug?”
Ad Auditory Digital
(Talking to Yourself) – This is where your eyes move when you’re having internal dialogue.
QUESTION: “Can you recite the Pledge of Allegiance?”
Typically, each time we use our neurology to gain access to a particular type of thinking, we move our eyes in the direction which facilitates our using that part of the neurology. The mind and body are absolutely interconnected, so each time we access our Visual Memory, for example, we move our eyes upward and to our left. (If you’re watching someone access Visual Memory, you will see them move their eyes upward and to your right.)
Based on our Model of Communication, and how we make an internal representation, you’ll remember that people rely on their 5 senses to make I/R’s about the world around them. Internally, we also generally come to depend on one representational system or modality more than another as we access information, and also use that information to create I/R’s. So, some people are using their Visual representational system more, some people use their Auditory representational system more, and some people use their Kinesthetic more than the others.
Usually an individual will prefer to use a certain modality of neuro linguistic programming or will use primarily a certain modality as what we call their primary representational system. Let’s go through the three major modes of operation so you can notice what mode people are operating in, and begin to identify them. You can then begin to match the modes by using the predicates and physiology that match their representational system.
Visual Neuro Linguistic Programming
Typically, people who are in a visual mode stand, or sit, with their heads and/or bodies erect with their eyes up, and will be breathing from the top of their lungs. They often sit forward in the chair or on the edge of the chair. They tend to be more organized, neat, well-groomed and orderly. More deliberate. More appearance oriented, and sometimes quieter. Good spellers. Memorize by seeing pictures, and are less distracted by noise. Often have trouble remembering verbal instructions, and are typically bored by long verbal explanations because their minds tend to wander. They would rather read than be read to. A visual person will be interested in how someone looks at them, and will respond to being taken places, and being bought things. They will tend to use words like: See ya later, I want to look at it, Focus on it, Watch it, Be clear, Foggy, Picture that, Notice, Appears.
Auditory Neuro Linguistic Programming
Someone who is auditory will move their eyes sideways and also down to the right. They breathe from the middle of the chest. They typically talk to themselves, and can be easily distracted by noise. They often move their lips when they say words to themselves. They can repeat things back to you easily. They may find math and writing more difficult and spoken language easier. They like music and learn by listening. They memorize by steps, procedures, and sequence. An auditory person is often interested in being told how they’re doing, and responds to a certain set of words or tone of voice. They tend to use words and phrases like: Listen, Talk to, Said, Speak, Hear, and Sounds like, “Good to talk to you.”
Kinesthetic Neuro Linguistic Programming
They will typically be breathing from the bottom of their lungs, so you’ll see their stomach go in and out as they breathe. Their posture is often more slumped over, and they often move and talk verrrry slooowly. They will typically access their feelings and emotions to “get a feel” for what they’re doing. They respond to physical rewards, and touching. They also stand close to people and touch them. They are often physically oriented people (athletes). They may move a lot, and they memorize by doing, or walking through something. They use words like: Feelings, Get in touch, Hold, Grasp, and Handle.
Fill in our form now and take advantage of this amazing opportunity to learn these techniques to improve your life and the lives of others as you do. Learn how to achieve your goals with The Tad James Company and learn how to improve people’s lives better than they currently are.
Call for help:
US Office (calling from outside the US):
1-702-440-4823
AU Office: 1-800-133-433
AU Office (calling from outside AU):
+61 (0)2 9221 9221
